Advantage of Varicocele Embolization
- Minimally invasive
- No stiches
- No internal cutting, bleeding or burning
- No general anesthesia
- No risks to testicular artery and nerve
- No risk of hydrocele
- Outpatient
- Quick recovery
Varicocele embolization is a minimally invasive treatment that utilizes the body’s anatomy to get to the abnormal veins without opening up the skin. This procedure is done in our outpatient center with twilight sedation. Absence of surgical incisions minimizes risks of infection and injury, allowing for a quick recovery.
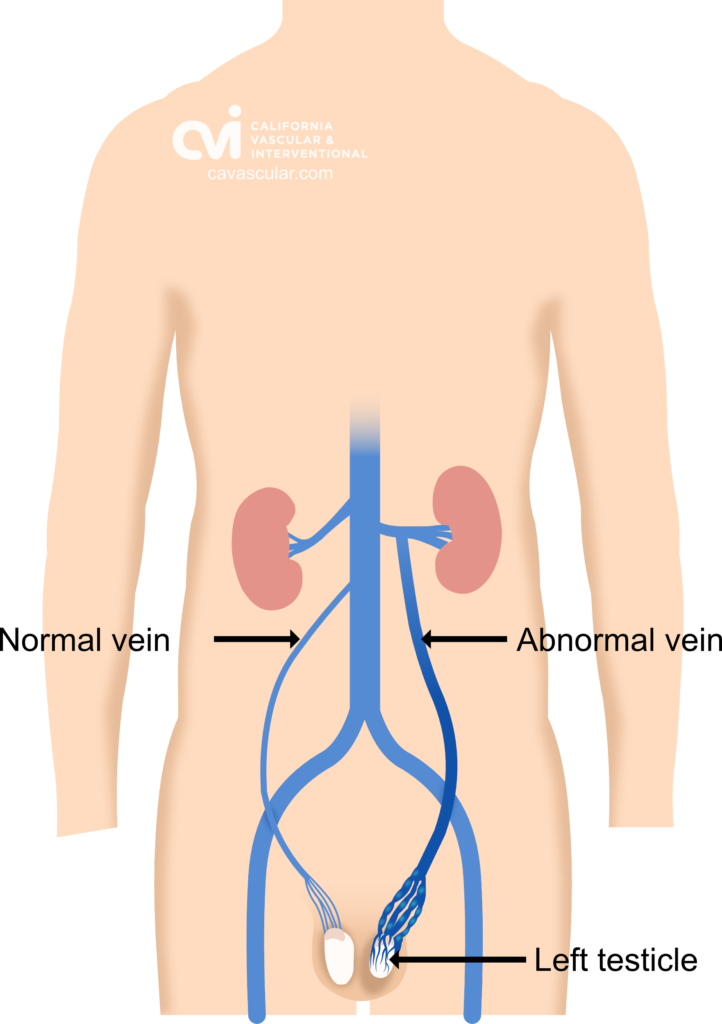
Varicocele: What is the Cause
The scrotum contains the testicles and epididymis, the place where your sperms are made and stored.4 Testicular veins drain the used blood out of the scrotum and back to the heart and lungs to be re-oxygenated. This allows for proper storage and development of the sperm.
When the valves regulating blood flow in the testicular vein turns defective, the blood backs up and the veins get bigger. Why is this an issue? This backed up blood is used blood, which can cause pain and affect temperature regulation. The stagnant blood flow leads to swelling of the testicular veins, which can be picked up on examination or ultrasound. Varicocele refers to abnormal enlargement of these abnormal testicular veins in the abdomen and scrotum.1 You can experience pain, discomfort, testicular shrinkage, and infertility.
Symptoms of varicocele include:
- Aching pain in scrotum during standing or activities
- Enlarged palpable scrotal veins
- Pain or pressure in the scrotal area
- Decreased sperm count or sperm function
- Shrinking of the testicle size over time
Men aged between 15 and 35 are more vulnerable to varicocele, which affects almost one in every 10.5 About 30% of cases of male infertility are due to a varicocele. Varicocele embolization helps treat the problem and restore blood flow as well as fertility.6
What is Varicocele Embolization?
Varicocele can be treated by embolization or surgery. Embolization is a non-surgical, outpatient, minimally invasive technique that uses x-ray guidance to see inside the body. This allows the treatment to be done without opening up the body. Embolization is the process of blocking the blood flow through these abnormal veins.
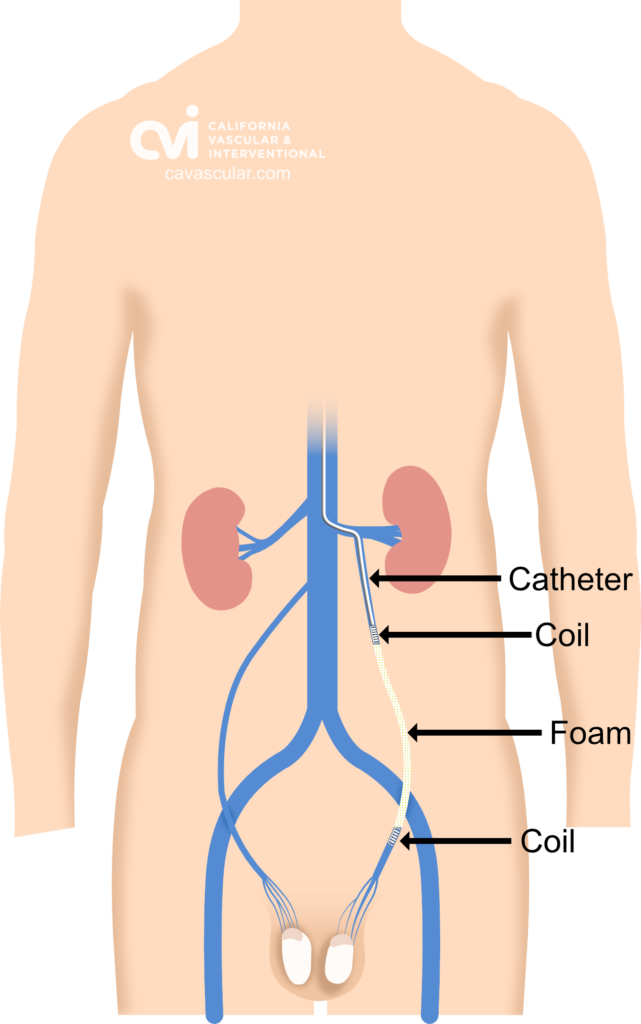
For varicoceles this is done by placing special foam and plugs (called coils) to block the blood flow in the abnormal veins.2,3 A successful varicocele embolization diverts blood into normal veins, preventing blood from pooling backwards into the scrotum. Once the flow is corrected and the varicocele is no longer present, symptoms improve.
Am I a candidate for Varicocele Embolization?
Treatment is offered for males who have:
- Fertility problems (low sperm count and malfunction)
- Pain
- Boys with a smaller testicle; at a higher risk for fertility problems when they are older
More than
More than
Request an Appointment
Please note that although we strive to protect and secure our online communications, and use the security measures detailed in our Privacy Policy to protect your information, no data transmitted over the Internet can be guaranteed to be completely secure and no security measures are perfect or impenetrable. If you would like to transmit sensitive information to us, please contact us, without including the sensitive information, to arrange a more secure means of communication. By submitting this form you consent to receive text messages from CVI at the number provided. Msg & data rates may apply. Msg frequency varies. Unsubscribe at any time by replying STOP.
Non-Surgical Varicocele Embolization: What to Expect
Varicocele embolization is an image-guided procedure performed by our double board certified vascular and interventional radiologist. The procedure is highly effective and offers a non-surgical alternative to surgery. It is less invasive and the patient is discharged within an hour after the procedure. The procedure is done through a small pinhole nick in the skin. Wide surgical incision and stitches are not required.
During the procedure the patient lies on their back on the procedure table. Some mild sedative is given through an IV to relieve any anxiety during the procedure. A small area in the neck or groin is cleaned and a local anaesthetic is used to numb the skin. A tiny skin nick is made and a tiny tube is put into the vein in the neck or upper thigh using ultrasound image guidance.
Our doctor will then take pictures of the veins using a contrast dye to visualize the anatomy and find the abnormal vein. Once in the abnormal vein, special foam and coil plugs are place through a tiny tube called a catheter. Platinum coils, gelatine sponge, and sclerosing agents are the most commonly used blocking agents for the procedure. 7
The catheter is then removed and a Band-Aid is applied. Varicocele embolization procedure typically takes an hour to complete. The patient is discharged typically after an hour of observation.
Suitable Candidate for Varicocele Embolization
Anyone with symptoms of a varicocele is a candidate for varicocele embolization. You are a suitable candidate for varicocele embolization if you have:
- Aching pain in scrotum during standing or activities
- Enlarged palpable scrotal veins
- Pain or pressure in the scrotal area
- Decreased sperm count or sperm function
- Shrinking of the testicle
- Infertility due to a varicocele8
Prior to candidacy the diagnosis needs to be confirmed by ultrasound.
Non-Surgical Varicocele Embolization: Preparation
Preparation for embolization is rather simple. No eating or drinking eight hours prior to your procedure time. Adequate hydration with water the day prior helps the kidneys flush the contrast dye after the procedure. Get rest and avoid stressful activities the week of your procedure. If you have a fever or new infection you would be asked to post-pone the procedure. Avoid alcohol and smoking 24 hours before the procedure and avoid resuming until 2-3 days after. Often patients’ are advised to stop blood thinners and NSAIDs a day before the procedure. Pre-existing health issues, allergies, and ongoing medication will be reviewed to make sure it is suitable for the procedure. Plan for a responsible adult to drive you to and pick you up from the facility.
Varicocele Embolization vs Surgery
Varicocele embolization presents an effective alternative to surgery. While the rate of success is almost the same, it provides many advantages over surgical intervention. These include:
- Minimal invasive procedure
- Outpatient procedure
- Faster recovery
- No stitches
- No internal cutting, bleeding or burning
- No hospitalization
- No general anesthesia
- No risks to testicular artery and nerve
- No risk of hydrocele
Non-Surgical Varicocele Embolization: Recovery
Patients are discharged home typically after a one hour observation. Rest is recommended the first 24 hours due to the IV sedation. Patients can resume normal activities the next day. Strenuous activities and exercise should be avoided for 2 to 3 days. There can be some mild aching after the procedure along the abdomen for a few days. Typically an anti-inflammatory medication or over the counter pill suffices for the discomfort; it is unlikely to need narcotic medication as with surgery.
Non-Surgical Varicocele Embolization: Risks and Limitations
In the hands of our experienced vascular and interventional radiologists this is a very low risk procedure. Bruising at the access site can occur. In untrained hands there can be a risk of coil misplacement. Improper sizing of the coils could result in migration or movement of the coils out of the vein. Recurrence can occur if all of the abnormal veins are not recognized and treated.
Our double board certified specialist is an expert in varicocele embolization and has treated numerous patients successfully. Request a consultation today to meet with our specialist.
Varicocele Embolization Success Rate
Varicocele embolization has a high success rate of over 90%, similar to surgery. Varicocele embolization has been performed for over 20 years with an excellent safety record. The safety and effectiveness has been demonstrated in several large trials.

We are Here to Help
Request an Appointment to meet with our varicocele specialist who will review your imaging, labs and history to determine if you are candidate for the procedure, and the outcomes you can expect. Each person is an individual and should discuss the potential risks and benefits of embolization and other treatments with our doctor to decide which option is best.
Appointments are available via an online video telehealth platform or in person at one of the offices in Los Angeles, Orange County or San Diego. Why should you choose us? Read here
1.) Leslie SW, Sajjad H, Siref LE. Varicocele. [Updated 2021 Feb 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448113/
2.) Embolization for Bleeding, Radiology, Michigan Medicine, University of Michigan Health, Retrieved, Jul 7, 2021
3.) Talaie R, Young SJ, Shrestha P, Flanagan SM, Rosenberg MS, Golzarian J. Image-Guided Treatment of Varicoceles: A Brief Literature Review and Technical Note. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2016;33(3):240-243. doi:10.1055/s-0036-1586140
4.) Garcia RA, Sajjad H. Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis, Scrotum. [Updated 2021 Feb 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549893/
5.) Varicoceles, Urology Care Foundation, American Urological Association, Retrieved on Jul 6, 2021
6.) Prasivoravong J, Marcelli F, Lemaître L, et al. Beneficial effects of varicocele embolization on semen parameters. Basic Clin Androl. 2014;24:9. Published 2014 May 16. doi:10.1186/2051-4190-24-9
7.) Favard N, Moulin M, Fauque P, et al. Comparison of three different embolic materials for varicocele embolization: retrospective study of tolerance, radiation and recurrence rate. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2015;5(6):806-814. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2223-4292.2015.10.10
8.) World Health Organization. (1992). The influence of varicocele on parameters of fertility in a large group of men presenting to infertility clinics. World Health Organization. Fertility and Sterility, 57(6), 1289–1293.
The above information explains what is involved and the possible risks. It is not meant to be a substitute for informed discussion between you and your doctor but can act as a starting point for such a discussion.